Before diving into the tools, it’s worth understanding what each one does and how they relate to each other.
LangChain: the logic engine
LangChain is, in short, a tool that allows AI to think with context.
It is available in Python and JavaScript and integrates easily with OpenAI, Anthropic, Ollama, and other models.
It connects language models (like ChatGPT) with your own data sources: documents, databases, APIs, or even websites.
That way, your AI can answer questions about your business or data, not just general knowledge.
Imagine you have a chatbot and you want it to answer questions about your products or clients.
LangChain acts as a bridge: it takes the question, searches for the necessary information, and generates a coherent answer.
The best part is that you can define each step of the reasoning process. For example:
- Analyze what the user said.
- Search for the necessary information.
- Generate a response with a specific tone.
- If it doesn’t understand, ask for more context.
All of this is structured as a logical chain of steps (hence the name Lang–Chain, “language chain”).
It not only connects data but also lets you design how the model thinks and acts, like building an intelligent flow diagram.
LangGraph: the next level
LangGraph is an evolution within the LangChain ecosystem.
It is designed to build more complex and dynamic flows, where the AI doesn’t just follow a linear path but makes decisions.
Why is it called Graph?
Because it literally works like a graph: a map with points (nodes) connected to each other.
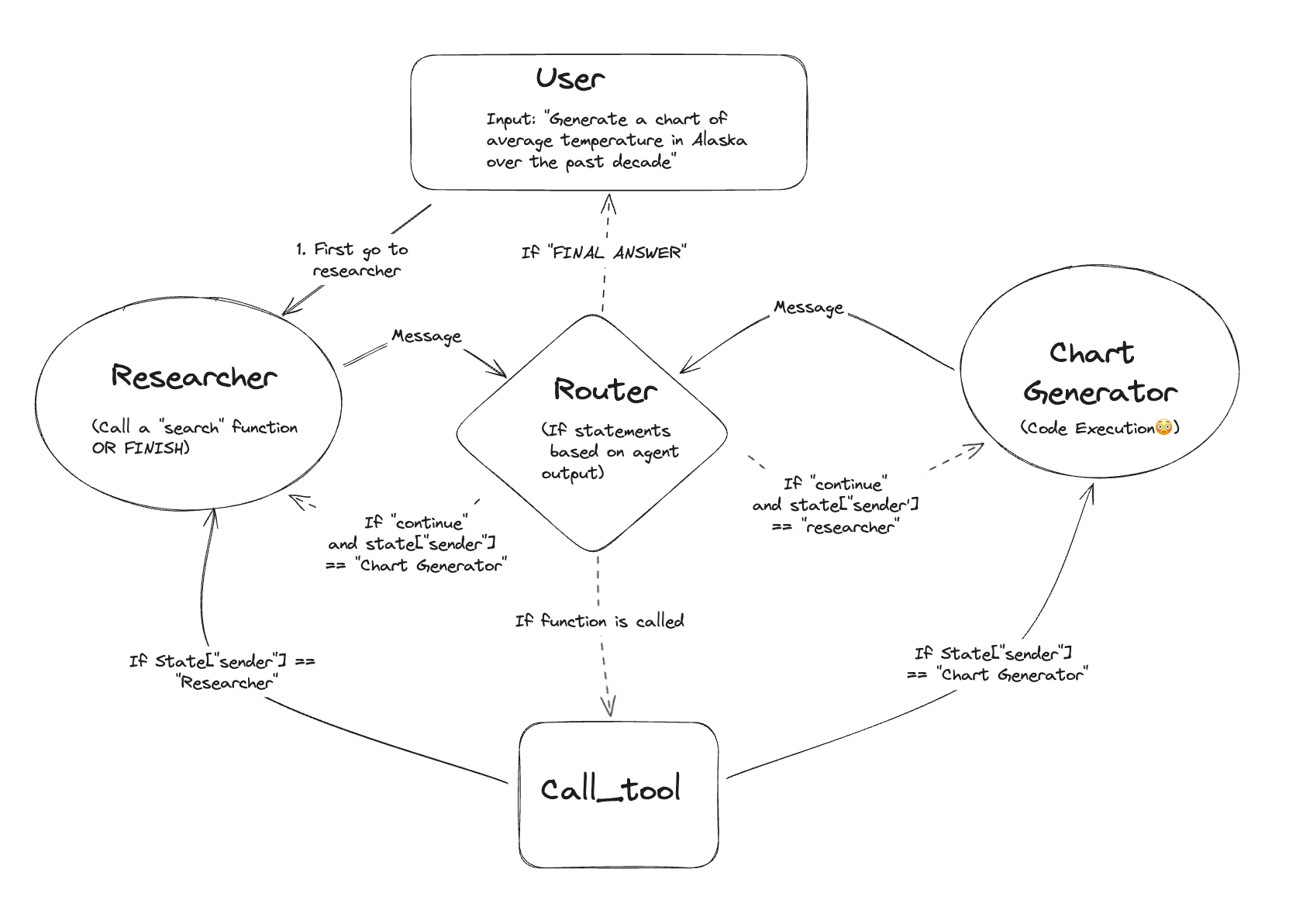
Each point represents an action or decision, and the lines show possible paths.
It’s also available in Python and JavaScript.
You can think of it like this:
- LangChain is linear — “first this → then that.”
- LangGraph is branched — a map of connected nodes with alternative paths.
Example:
- If the AI doesn’t understand → ask for clarification.
- If it detects “book appointment” → go to the booking flow.
- If it detects “cancel” → go to the cancellation flow.
Each node in the graph represents a state or action (greet, confirm time, register data, etc.), and the connections indicate what happens next.
In short:
LangGraph is like LangChain 2.0, designed for AIs that change state, adapt, and make decisions.
And best of all: both are open source.
What is an agent?
An agent is an AI capable of reasoning, deciding, and acting autonomously.
It doesn’t just respond with text—it analyzes context, executes actions, and chooses its next step.
LangGraph is perfect for this because its graph-based architecture allows you to represent:
- Agent memory
- Reasoning steps
- Alternative paths
- Condition-based decisions
This way, agents stop being linear flows and become systems with “mental states,” capable of moving according to the situation.
Ecosystem and tools
LangGraph has excellent documentation, clear examples, and an active community.
It includes LangSmith Studio, a visual tool to view and debug the graph in real time.
Companies like GitLab, Cisco, and Rakuten are already using it to build internal agents.
LangFlow
LangFlow is another piece of the ecosystem, designed for people who prefer to build flows without writing much code.
You can think of it as a visual AI builder: drag, drop, and connect blocks instead of writing Python.
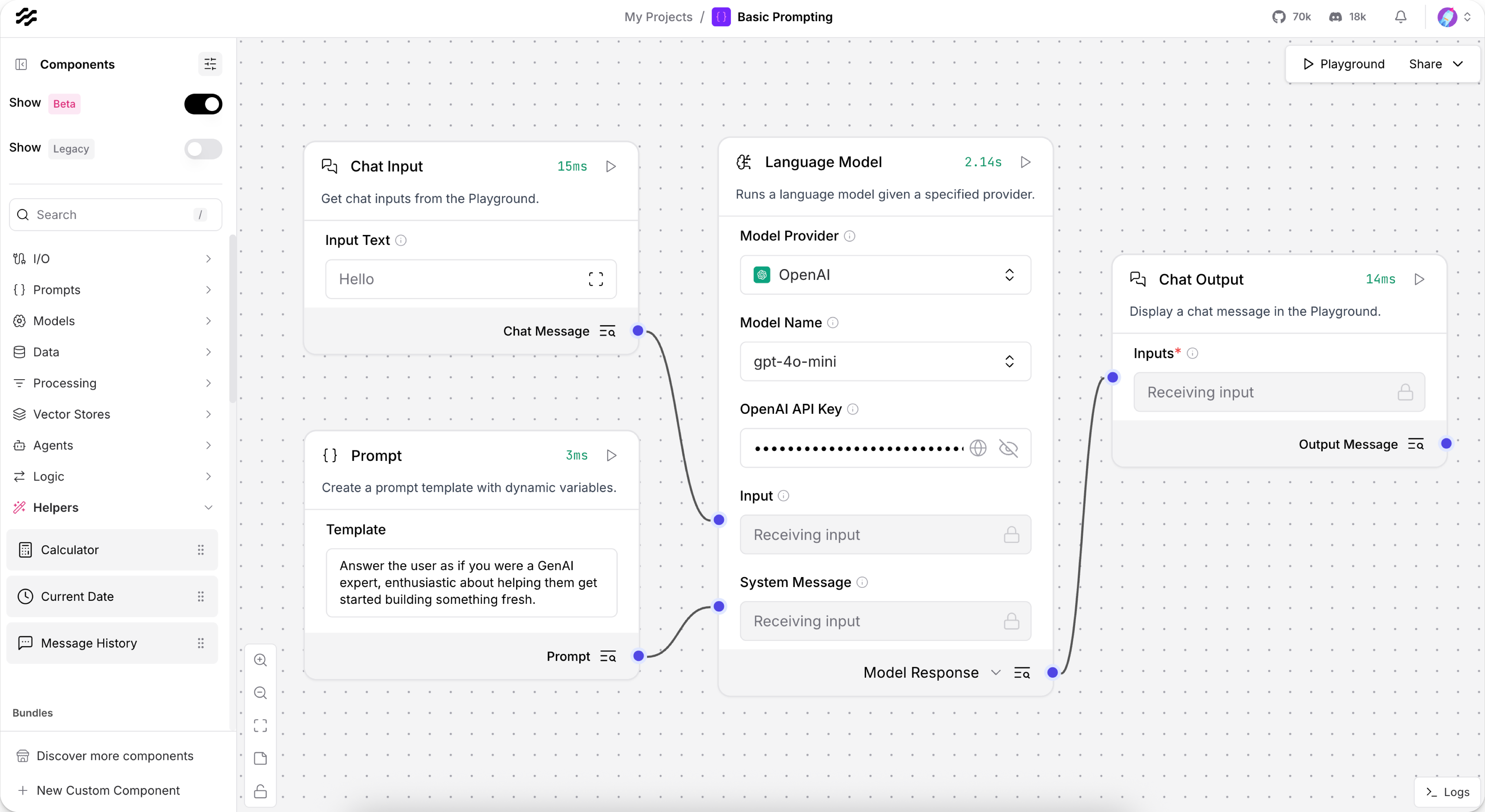
The downside: it is limited by the interface.
You can only do what the UI allows, and it’s harder to integrate with large or custom systems.
Comparison: LangChain vs LangGraph vs LangFlow
Flow control:
- LangChain works step by step in a linear way.
- LangGraph offers full control: you can define nodes, decisions, and memory.
- LangFlow is limited to what the visual interface allows.
Complexity:
- LangChain is ideal for simple or medium-complexity flows.
- LangGraph is built for complex and dynamic agents.
- LangFlow is perfect for quick prototypes or testing ideas.
Integration:
- LangChain connects easily with APIs or databases.
- LangGraph integrates well with backends like FastAPI or Flask.
- LangFlow is less flexible for production environments.
Code vs Visual:
- LangChain and LangGraph are fully code-based, though LangGraph includes visual flow representation.
- LangFlow allows no-code visual building.
Conclusion
LangChain is the foundation: the logical structure and the heart of the flow.
LangGraph is the next step: a stronger version designed for agents that think, decide, and adapt.
LangFlow is the visual option: ideal for building without code and experimenting quickly.
Each tool has its own purpose, and they all revolve around LangChain.
Best of all, all three are open source. 🤩